The content of the article
Any disease in a baby is perceived several times more serious, since the baby is small and the consequences can be very different. Moreover, the child can not talk about his feelings and expresses pain by crying. One of the most unpleasant diseases at any age is stomatitis. Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa, which is manifested by various rashes, large ulcers or white plaque. Stomatitis can be different, depending on the pathogen. Stomatitis occurs in infants quite often, because the small body does not yet have a strong immune system that can withstand external stimuli. Moreover, the mucous membrane in the crumbs' mouth is still so thin and delicate that it reacts to almost any irritant. In this article we will learn to distinguish between types of stomatitis, determine the disease according to the symptoms of the baby, learn about the causes and methods of treating this ailment.
Types of stomatitis and the reasons for their development
To know the causes and methods of treating stomatitis, you need to clearly determine the origin of the disease, this can be done by the appearance of damage to the mucosa.
- Candidiasis stomatitis. This is the most common type of stomatitis in babies in their first year of life. Candidiasis stomatitis is caused by Candida bacteria, it’s simply thrush. Most often, the baby becomes infected with candidiasis from the mother with insufficient hygiene or when passing through the birth canal. Often, Candida lives in the body in moderation, but begins to become active with a decrease in immunity, hypothermia, etc. This is considered a fungal disease. Such stomatitis is characterized by a whitish coating on the cheeks, gums, palate, tongue. As a rule, plaque can be removed, in its place remains a little pinkish from inflammation of the mucosa. Candidiasis can also develop after taking antibiotics.
- Aphthous stomatitis. Aphthous stomatitis is a fairly large sores, with clear boundaries. Ulcers most often form on the gums, tongue, cheeks. The color of the ulcer is whitish. This type of stomatitis brings severe pain, often the baby cries without stopping. Aphthous stomatitis can occur in children and adults, most often it indicates a decrease in immunity and a deterioration in the body's defenses. Often, such stomatitis occurs against the background of other serious diseases.
- Herpetic stomatitis. Herpetic stomatitis is caused by the herpes virus. The baby can be infected in utero from the mother or after birth through contact with sick adults (kiss, licking the nipples, etc.). Antiviral drugs must be used to treat the disease. After infection, it is no longer possible to completely get rid of the virus, it is simply suppressed by treatment and can be activated again when the body's defenses are weakened. Herpetic stomatitis is easy to identify by small and numerous sores similar to vesicles.
- Allergic stomatitis. This type of stomatitis develops due to an allergic reaction of the body to certain foods and materials. The baby can react to a poor-quality toy, which he often takes in his mouth, a new nipple, or even complementary foods.
Sores in the child’s mouth can be due to non-compliance with oral hygiene, if the baby pulls everything in his mouth, the nipples, bottles, and mother’s breasts are not processed well enough. Stomatitis can occur against the background of a new feeding, in which there is too much sugar. The disease can develop on the background of injuries of the oral mucosa.If the doctor doubts the origin of stomatitis, he can prescribe a laboratory test, during which a smear or scraping from the baby's ulcer is taken. Identification of the pathogen will help to prescribe a more targeted and effective treatment. But how can a young mother suspect stomatitis?
How to recognize stomatitis
Of course, the appearance of wounds on the oral mucosa can be considered the main symptom of the disease. But what makes an inexperienced mother look into the baby's mouth? What precedes the appearance of ulcers?
- The baby's mood changes. He does not laugh, often cries, becomes moody and irritable, sleeps poorly, it is difficult to calm him down. Such symptoms speak of many diseases, but they are already a bell - something is wrong with the baby.
- In a child with stomatitis, the temperature can rise, and quite high. It can occur even before ulcers in the mouth occur.
- The gums themselves become inflamed, red, swollen. When you touch the baby cries, this indicates tissue soreness. Small vesicles may appear on the mucous membrane, which subsequently burst and ulcers form in their place.
- If you try to remove plaque with your finger or a clean cotton wool, an inflamed area of the mucosa that can bleed remains in its place.
- Salivation becomes unusually active - the body tries to wash off the inflammation on its own.
- The baby refuses to suckle, because while eating, the child experiences increased pain.
- The kid often pulls the handle in his mouth.
- Sometimes a child may get bad breath.
Already closer to the year, the baby can show with his finger where it hurts. But until this time, self-diagnosis is quite difficult. Be sure to show the child to the doctor, an experienced doctor will be able to recognize the disease.
Medication for stomatitis
Depending on the type of stomatitis, treatment can be completely different. Here are some medical directions that are commonly used in the fight against stomatitis.
- Antiviral agents. If the disease is caused by the herpes virus, then antiviral drugs and ointments are needed to treat stomatitis. Among them, Acyclovir, which is available in the form of tablets and ointments. It is just aimed at combating herpes. In addition to it, you can highlight Tebrofenova and Oxolinic ointment, which you probably have in your home.
- Antifungal drugs. Antifungal drugs are used in the fight against candidal stomatitis. Among the most effective are Nystatin, Levorin and Futsis. Be sure to pay attention to the fact that these should be children's forms of medicine that are acceptable for use at your age.
- Antihistamines. For allergic stomatitis, antihistamines are used - Zodak, Diazolin, Suprastin. They help reduce the body's response to the pathogen, relieve swelling, itching and redness.
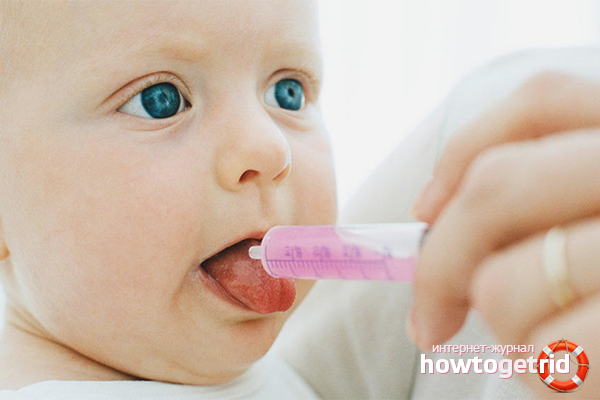
- Painkillers. It is imperative to use painkillers that will help the baby survive the disease, eat and sleep normally. After using painkillers, the mouth may become a little numb, which will affect the quality of the sucking. However, after some time the sensation disappears. Among the acceptable ointments and gels are Kamistad, Propolis spray, Kalgel. Pay attention to any pain medication, they must be acceptable at your age. After all, the baby simply swallows many funds - they must be safe when taken orally.
- Healing. With prolonged stomatitis or too large ulcers, the doctor may prescribe healing ointments, for example, Solcoseryl.
- Antipyretic drugs. If stomatitis proceeds with a temperature increase of more than 38 degrees, you need to resort to antipyretic drugs. Among them are Ibuklin, Ibufen, Paracetamol (for children), Nurofen, etc.
Antibiotics in the treatment of stomatitis are usually not used, only in the most difficult cases, when the disease is caused by a malfunction of the internal organs. If stomatitis does not go away when treated with local antiseptic agents, antibacterial ointments are prescribed. Dosage and a specific drug can only be prescribed by a doctor. Do not self-medicate in any case.
How to treat stomatitis in infants
In addition to medical appointments, there are many important recommendations that will help you accelerate recovery and get rid of stomatitis in a matter of days.
- Observe oral hygiene - thoroughly wash and process bottles, nipples, toys. During the period of illness, wash your breasts after each feeding. This will protect the baby from re-infection.
- Since stomatitis is often viral, you need to provide your child with plenty of water. Give the baby a chest without restrictions, offer water, at least for the period of illness. The faster the virus is washed out of the body, the sooner the baby will recover. If the baby is already receiving complementary foods, in his diet should be a warm broth, apple juice (diluted with water), jelly. These are simple drinks that do not cause mucosal irritation.
- Humidify the room - wash the floor, open the windows. The room should have clean and cool air without dust.
- If the baby is already eating complementary foods, pay attention to food. Food should be at the optimum temperature (neither hot nor cold), so as not to irritate the mucous membranes of the crumbs. Discard mashed potatoes for a while - it irritates the mucous membrane. Do not add a lot of salt to food - it will bring pain. If the baby does not want to eat - do not force him. The main thing is that he drank a lot.
- Every 3 hours and after each meal, the child's oral cavity should be treated with antiseptics - Furacilin or Chlorhexidine. You can use simple baking soda. Dissolve a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm water. Wash your hands thoroughly and wrap a piece of sterile bandage on your finger, soak it in the prepared solution. Open your baby's mouth and carefully pass a finger along the cheeks from the inside, gums, tongue. No need to do the treatment immediately after eating - the baby may vomit. You can dip the nipple in an antiseptic and give crumbs, the medicine will surely spread throughout the oral cavity.
- Breasts are often given solid rubber toys, a crust of bread, and other items to scratch their gums. Give up this venture for the duration of the illness. Solid materials can cause pain in the inflamed areas of the oral cavity.
- If the baby already has several teeth, they must be cleaned using a small silicone brush with soft bristles. She puts on her mother’s finger and removes food debris and plaque from her teeth. If this is not done, the disease will last much longer.
- Follow the baby's hygiene. Since the baby pulls everything in his mouth, the surrounding objects should be clean - bedding, clothes, toys, mother's hands, etc. In no case do not allow pets to clothing and personal hygiene products of the child. Especially those who walk on the street.
- It is quite difficult to prevent herpes stomatitis in a child, since almost all are carriers of this virus. However, in order for the crumb body to withstand the disease, it is necessary to strengthen its immunity. From an early age, provide the child with proper nutrition, often walk with him in the fresh air, give the child massage and exercise therapy, temper, leaving the baby undressed for a few seconds.
- You can treat stomatitis with folk remedies. Blueberries have a good antibacterial effect - you can lubricate the child's oral cavity with its juice. Sores can be treated with a strong decoction of a string and calendula. They suppress inflammation, disinfect the wound, relieve pain, swelling and redness.
Pay attention to the symptoms in which you need to see a doctor as soon as possible.If the child’s condition does not improve after three days of treatment, if the baby becomes lethargic and lethargic, or vice versa, cries all the time and cannot sleep, if it becomes more difficult to bring down the body temperature, be sure to go to the pediatrician for a second appointment.
At first glance, stomatitis may seem insignificant, and suck is not a dangerous disease. Yes, they don’t die from stomatitis, but it brings so much inconvenience, pain and discomfort that any mother would be ready to take the disease upon herself, just to save her child from the torment. But do not despair. With proper treatment, stomatitis is quickly treated - in 2-3 days the baby will feel relief and will be able to eat, drink and sleep normally again, to the delight of anxious parents!
Video: how to treat stomatitis in a child







Submit